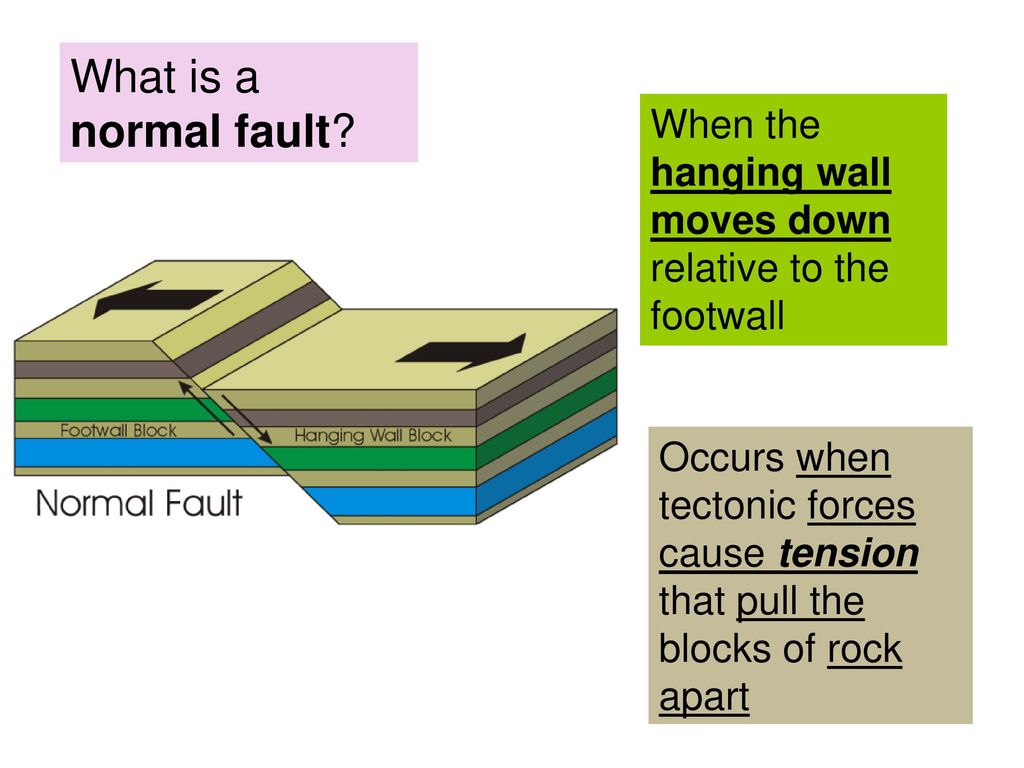
Fault The Hanging Wall Moves Downward Relative To The Footwall

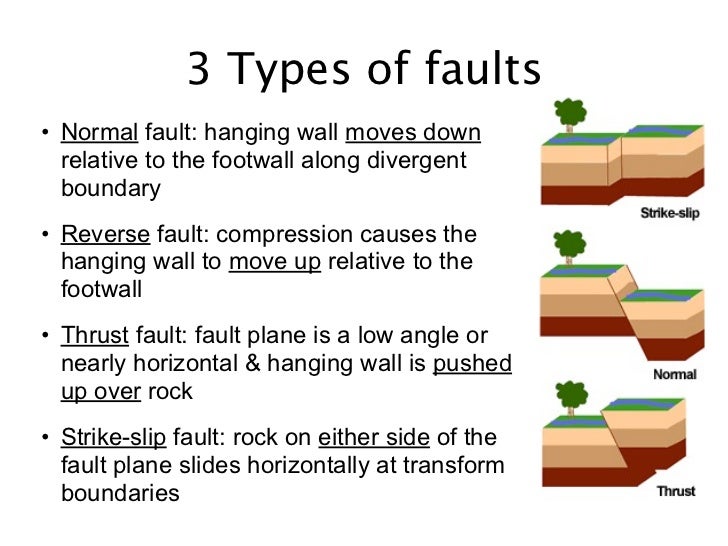
Strike slip faults are right lateral or left lateral depending on whether the block on the opposite side of the fault from an observer has moved to the right or left.
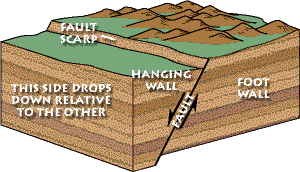
Fault the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall. In a normal fault the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall. Low angle normal faults with regional tectonic significance may be designated detachment faults. These usually occur when tectonic forces cause tension that pulls rocks apart. Formed by compressional stress rocks are pushed towards each other thrust fault.
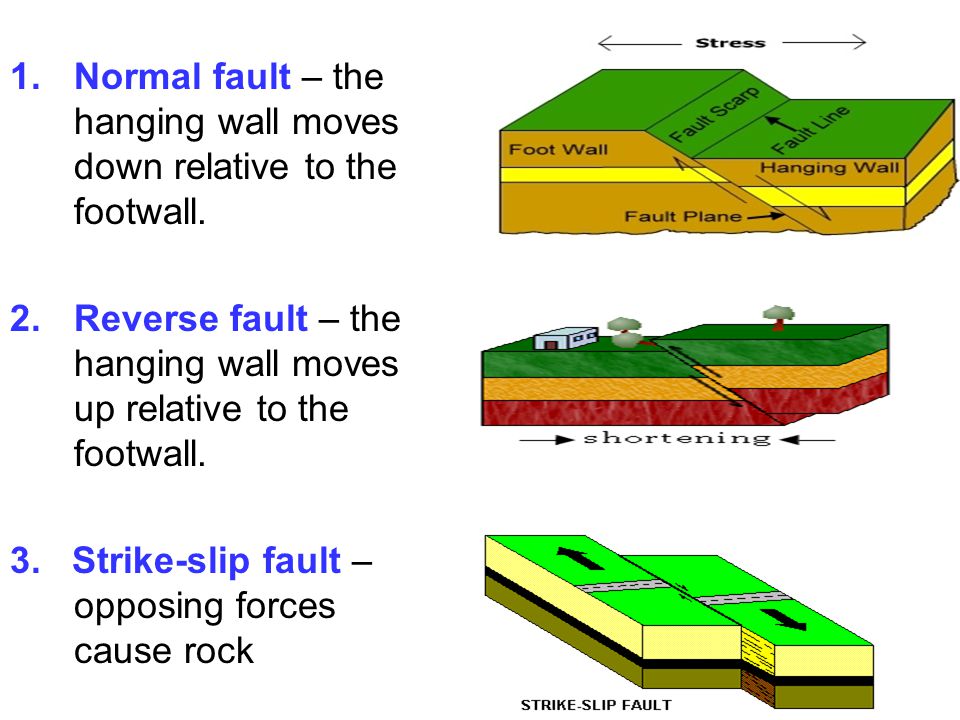
In this fault the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. When the hanging wall moves up in relative to the footwall it is called a fault. To the dip is called dip slip faulting. In dip slip faults if the hanging wall block moves downward relative to the footwall read more.
An upthrown block between two normal faults dipping away from each other is a horst. There is a normal fault which happens at a divergent boundary. It is caused by tension. In this fault the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall.
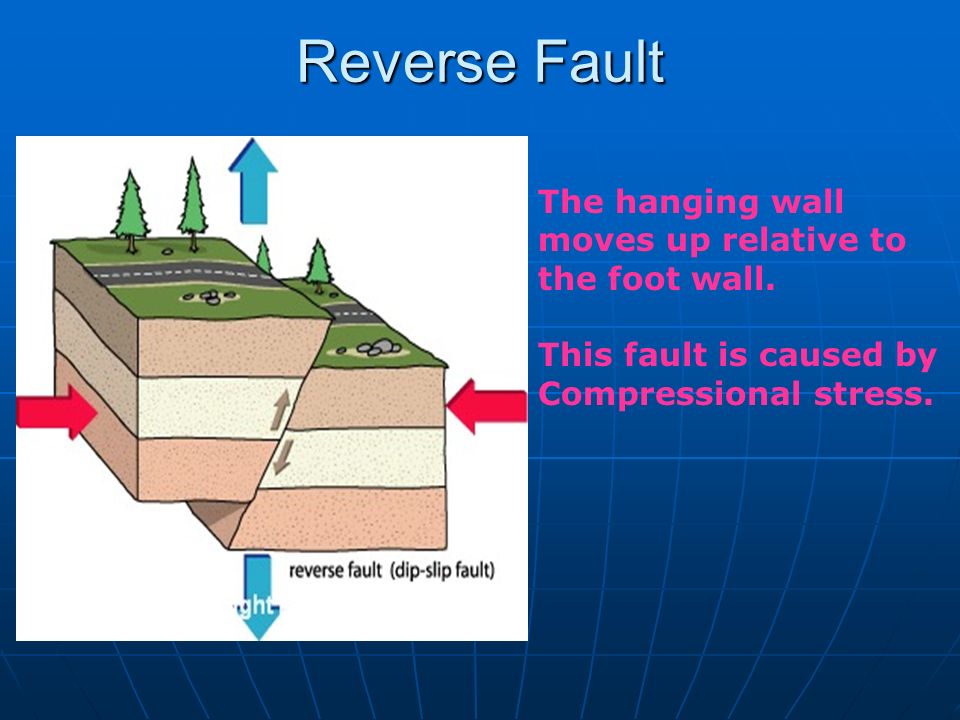
The hanging wall moves down relative to the foot wall. When the hanging wall moves down in relative to the footwall it is called a fault. Special type of reverse fault that is nearly horizontal angle has less than 45 degrees strike slip fault. The hanging wall moves up relative to the foot wall.